
Definition of ‘Engine’:
 An engine is a device which transforms one form of energy into another form.
An engine is a device which transforms one form of energy into another form.
Normally, most of the engines con-vert thermal energy into mechanical work and therefore they are called ‘heat engines’.
Heat engine is a device which transforms the chemical energy of a fuel into thermal energy and utilizes this thermal energy to perform useful work. Thus,thermal energy is converted to mechanical energy in a heat engine.
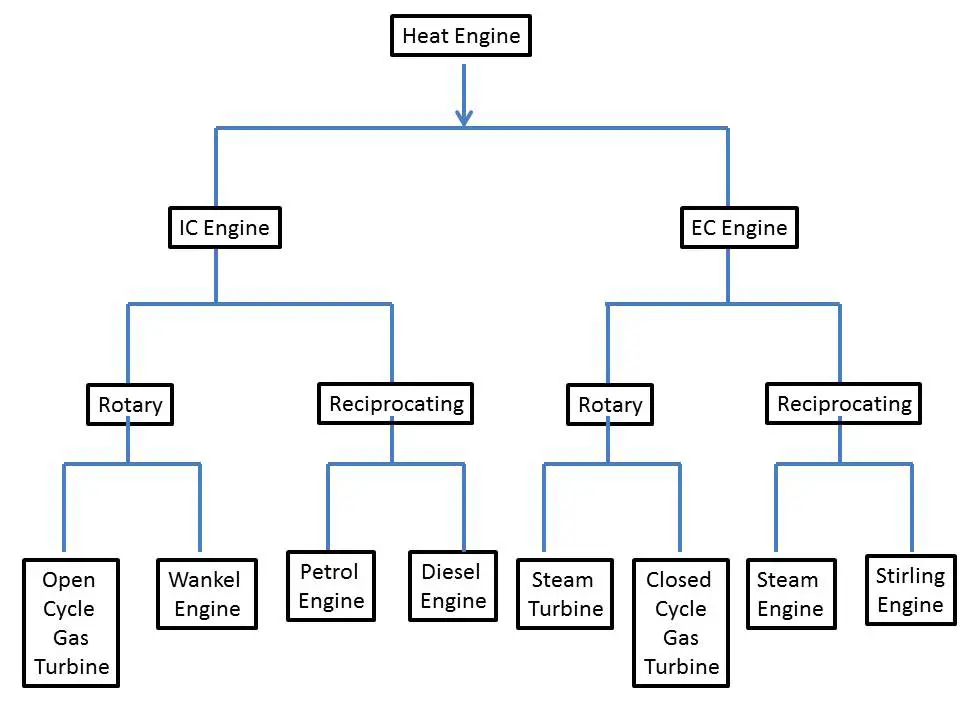
Heat engines can be broadly classified into two categories:
(i) Internal Combustion Engines (IC Engines)
(ii) External Combustion Engines (EC Engines)
Classification of Heat Engines:
Engines whether Internal Combustion or External Combustion are of two types:
(i) Rotary engines
(ii) Reciprocating engines
Rotary Engine:
A rotary engine is an internal combustion engine, like the Engine in your car but it works in a completely different way than the conventional piston engine.
In a piston engine, engine works four different jobs -- intake, compression, combustion and exhaust. A rotary engine does these same four jobs, but each one happens in its own part of the housing. example are Wankel Engines.

Rotary engines have a low thermal efficiency as a result of a long combustion chamber and unburnt fuel making it to the exhaust.
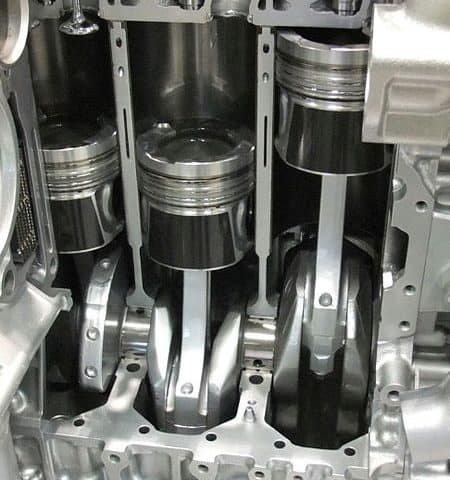
Reciprocating engines:
an engine in which the to-and-fro motion of one or more pistons is transformed into the rotary motion of a crankshaft.
The reciprocating internal combustion engines have been found suitable for use in automobiles, motor-cycles and scooters, power boats, ships, slow speed aircraft, locomotives and power units of relatively small output.


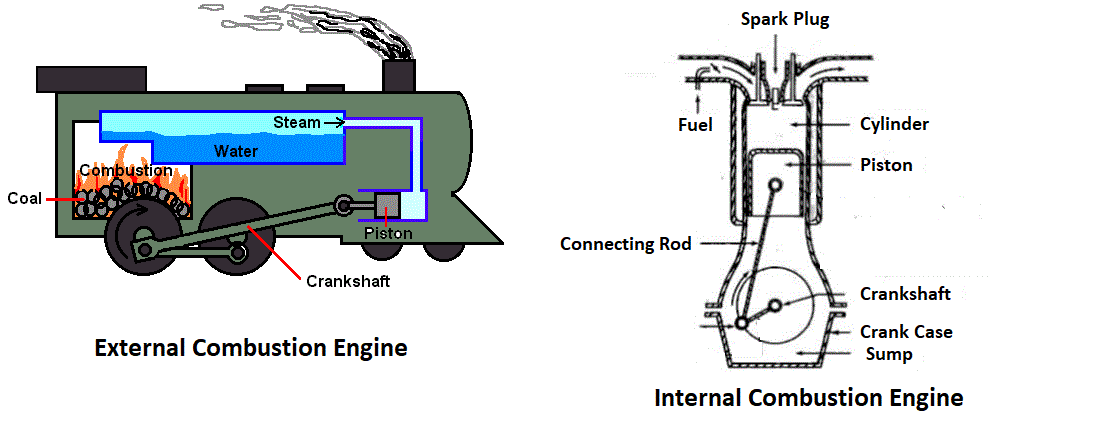
External Combustion and Internal Combustion Engines:
External combustion engines are those in which combustion takes place out-side the engine whereas in internal combustion engines combustion takes place within the engine.
For example- in a steam engine or a steam turbine, the heat generated due to the combustion of fuel is employed to generate high pressure steam which is used as the working fluid in a reciprocating engine or a turbine. In case of gasoline or diesel engines, the products of combustion generated by the combustion of fuel and air within the cylinder form the working fluid.
Comments